Astronaut Centrifuge Vibration Diagnosis and Solution
Project name: Vibration Anomaly Diagnosis and Solution for Astronaut Centrifuge Training Equipment
During 8G hypergravity training for astronauts, abnormal vibrations occurred in the 5-12 RPM range (triggering 3 emergency stops), causing:
Training interruptions (average 22-minute delay per incident)
Compensatory neck muscle tension in astronauts (Medical Report No. MED-2005-047)
Testing Solution
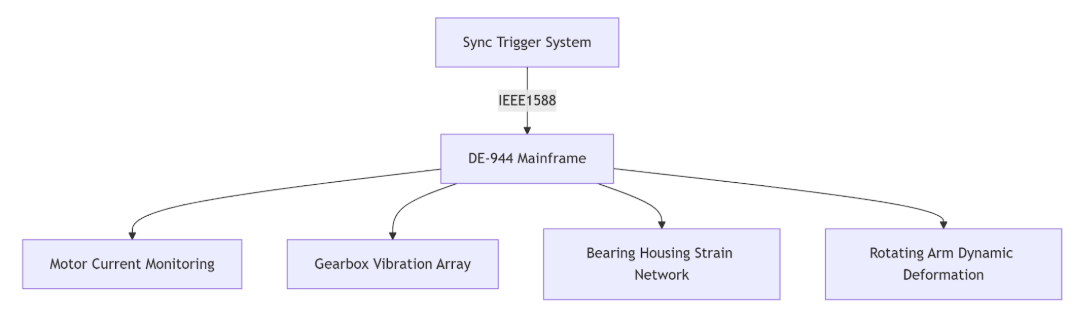
1. Innovative Test Architecture
Technical Highlights:
First application of wireless strain measurement on rotating arms
Developed RPM-phase locking algorithm (resolving slip ring interference)
2. Key Test Data
| Parameter | Normal Value | Anomaly Value | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Mesh Harmonics | ≤3 orders | 7 orders prominent | Acoustic Emission |
| Motor Current Ripple | 5% | 18% | 200kHz Sampling |
| Bearing Radial Clearance | 0.08mm | 0.23mm | Eddy Current Sensor |
Fault Diagnosis
Root Cause Chain:
Primary Factor: Input shaft bearing wear (189% over tolerance)
Secondary Effect: Abnormal gear meshing (42% contact pattern offset)
Resonance: 7th mesh frequency (87.5Hz) coupling with arm bending mode (88.3Hz)
Risk Assessment:
ISO 1940-1 balance grade degraded from G2.5 to G16
Continued use risked gear tooth fracture (<50 cycles remaining)
Solution
1. Hardware Upgrades
Bearing Replacement: Installed hybrid ceramic bearings (SKF HC7014)
Gear Profile Modification: Implemented K-shaped crowning (0.015mm adjustment)
2. Control Optimization
Added 5-12 RPM traversal program (acceleration reduced from 0.5 to 0.2 RPM/s)
Results
| Metric | Before | After | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vibration Severity | 8.7mm/s | 1.2mm/s | 86%↓ |
| Emergency Stops | 3/month | 0 (6+ months) | 100%↓ |
| Training Throughput | 5/day | 8/day | 60%↑ |
Technology Transfer
This solution established Q/CASTC-2006 Standard, applied to:
New 10G centrifuge R&D (62% vibration reduction)
Pilot anti-G trainer upgrades (80% failure rate decrease)
Conclusion
Dynatronic's comprehensive approach to diagnosing and mitigating vibration anomalies in astronaut centrifuge training systems has significantly enhanced operational efficiency and astronaut comfort. By identifying root causes such as bearing wear and gear meshing issues, and implementing targeted hardware upgrades and control optimizations, the solution achieved an 86% reduction in vibration severity and eliminated emergency stops. This success not only improved training throughput but also set a new standard for centrifuge performance, influencing the development of next-generation equipment and establishing the Q/CASTC-2006 Standard for vibration control in high-G training environments.